The recent imposition of a 25% tariff on heavy trucks not manufactured in the U.S. marks a significant development in the trucking industry, sending ripples through both truck manufacturing and transportation sectors. Expected to take effect on October 1, 2025, this tariff stands to reshape the competitive landscape for domestic truck manufacturers such as Paccar, Mack Trucks, and Volvo, who will now have a buffer against foreign competitors. However, alongside this protective measure comes the reality of increased costs, as manufacturers grapple with the potential need to raise truck prices to offset the tariff’s impact.
For the trucking industry, especially smaller transport companies operating on tight margins, the rise in vehicle costs may prove to be a considerable burden. With experts estimating that a new Class 8 truck could see price increases of around $30,000, operators face harsh choices in fleet expansion and operational budgets. As tariffs in other sectors have already strained resources, stakeholders in the trucking business must navigate this new challenge, heightening concerns not just for profitability but for the overall health of the industry. This article will explore the far-reaching implications of this tariff, its impact on pricing, and what it means for the future of trucking in America.
Economic Rationale for the 25% Tariff on Heavy Trucks
The 25% tariff on imported heavy trucks is designed to support domestic production and secure American jobs in the trucking industry. This measure aims to combat low-priced imports that undermine the competitiveness of U.S. manufacturers. By raising the cost of foreign trucks, the government hopes to encourage consumers to purchase American-made vehicles. This, in turn, will help companies like Paccar, which manufactures Kenworth and Peterbilt trucks.
Potential Benefits for U.S. Manufacturers
U.S. manufacturers could gain from reduced competition as tariffs raise the cost of imports. With foreign trucks becoming more expensive, domestic companies might see increased sales and market shares. This opportunity could enable them to enhance production capabilities, leading to job creation within the industry. Moreover, by strengthening the manufacturing base, the economy stabilizes and promotes innovation within the domestic truck sector.
Impacts on Competition
While tariffs could provide temporary protection for U.S. manufacturers, they might also disrupt the supply chains that many companies depend on. Manufacturers sourcing parts from abroad could face higher costs, impacting their operations. Stellantis, for example, projected a loss of $2.68 billion due to the tariffs. This situation highlights how tariffs can lead to operational challenges and layoffs as companies adapt to rising costs.
Pricing Implications
Despite the protection offered by tariffs, truck prices are likely to rise. Estimates indicate that new heavy trucks may cost between $25,000 and $35,000 more. Given that the trucking industry operates on thin margins, these heightened costs could change consumer purchasing behavior. Fleet operators may delay new purchases or extend the lifespan of their current vehicles, ultimately decreasing demand. This presents a dilemma for domestic manufacturers as they balance job protection and affordability for consumers.
In conclusion, while the 25% tariff on heavy trucks aims to bolster U.S. manufacturers and shield them from foreign competition, it presents challenges that could affect operational viability and consumer purchasing decisions. Finding a balance between protectionism and free market principles is essential as the industry navigates these complex dynamics.
| Manufacturer | Pricing Strategy | Expected Profitability Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Paccar | Increased use of USMCA-certified parts and tariff surcharges | Positive; shares rose 6%, but expects $75 million in costs due to tariffs |
| Volvo | Laying off 550-800 workers, implementing tariff surcharges | Negative; facing high costs, leading to layoffs and production shifts |
| Mack Trucks | Similar approach to Volvo; parent company planning strategic layoffs and operational shifts | Negative; projected declines in demand and profitability |
| Freightliner | Adjust pricing in line with tariff impacts | Depends on U.S. market response to increased truck costs |

The Real-World Effects of Tariffs on Truck Pricing
Tariffs significantly impact truck pricing, as exemplified by the recent experiences of Volvo Trucks. In response to increasing costs stemming from tariffs on foreign-sourced components, Volvo announced a $3,500 tariff surcharge on new trucks. However, this surcharge does not fully mitigate the heightened expenses, leading to diminished profit margins for the company.
The American Trucking Associations projected that the 25% tariff on imported heavy-duty Class 8 trucks could increase the price of each vehicle by approximately $30,000, increasing financial burdens on companies operating on slim margins and potentially causing them to delay new purchases or extend the lifespan of their existing fleets.
In the first quarter of 2025, Volvo reported a 29% decline in net profit, a concerning figure in light of a 9% decrease in vehicle sales attributed to uncertainty surrounding tariffs and their ripple effects on global trade. Consequently, the company adjusted its forecast for heavy-duty truck sales in North America downward by 25,000 units, projecting 275,000 vehicles.
To navigate the effects of these tariffs, Volvo has announced layoffs of between 550 and 800 workers across several U.S. locations, further reflecting the operational strain that tariffs have imposed on its workforce and business strategy.
Looking ahead, the U.S. government is set to impose a 25% tariff on all imported medium- and heavy-duty trucks beginning November 1, 2025, raising further concerns for companies like Volvo that depend on imported components.
In summary, the tariffs on truck imports have compelled manufacturers like Volvo to increase prices through surcharges, face significant reductions in profitability, and adjust their operations through workforce reductions to remain viable in a challenging market. This scenario paints a broader picture of the trucking industry’s struggle to maintain equilibrium amid legislative pressures and fluctuating global trade conditions.
User Adoption Data Statistics in the Trucking Market Post-Tariffs
The implementation of tariffs in the trucking sector has induced significant changes that can be quantified through various statistics affecting user adoption, purchases, and operational strategies. Here are the key findings:
Truck Purchases and Fleet Management
- Decline in Truck Deliveries: Companies like Volvo Group have adjusted their forecasts for heavy truck deliveries in North America, projecting 265,000 units for 2025, a decrease of 10,000 units from earlier estimates. This contraction is mainly attributed to declining freight volumes, high tariff costs, and regulatory uncertainties. [Source: Reuters]
- Fleet Reductions: In light of challenging market conditions, carriers have reduced their fleets by an average of 2.2%. For example, Marten Transport slashed its total fleet from 3,126 tractors to 2,928 over the span of a year, indicating a cautious approach towards fleet expansion amidst rising costs. [Source: CCJ Digital]
Consumer Behavior and Market Shifts
- Rise of Private Fleets: There has been an 11.7% year-over-year increase in shipments from private fleets in 2024, reflecting shippers’ preference for tighter control over their logistics amid tariff uncertainties. This trend demonstrates a shift away from reliance on traditional freight carriers towards more secure, self-managed transport solutions. [Source: Entourage Freight Solutions]
- Freight Volume Fluctuations: The trucking industry saw a temporary boom in shipments due to stockpiling ahead of tariff implementations. Nevertheless, this was succeeded by a downturn, with national shipments down 9.8% and spending falling by 4.9% in the second quarter of 2025 compared to the same quarter the previous year. [Source: Food Logistics]
Overall Market Dynamics
- Increased Operational Costs: The tariffs have raised the cost of truck manufacturing and maintenance, with estimates suggesting that a 25% tariff could inflate tractor prices by approximately $35,000. Larger fleets particularly feel the strain, which affects their annual operational budgets heavily. [Source: Fleet Connection]
- Declining Port Activity: U.S. ports project a decrease in import volumes, anticipating container imports to dip below 2 million TEUs monthly through late 2025. This reduction directly influences trucking demand, especially in facilities reliant on drayage and intermodal transport. [Source: Luna Logistics]
In conclusion, the post-tariff landscape has led to diminishing truck purchases, strategic cutbacks in fleet sizes, an inclination towards private logistical solutions, and surging operational expenses—all of which are reshaping the U.S. trucking market significantly.
As the trucking industry faces the ramifications of the newly imposed tariffs, it is evident that strategic planning has never been more critical. Truck manufacturers must act decisively to adapt their strategies, not just in response to the tariffs, but also to the shifting landscape of market dynamics. This adaptation should encompass a multifaceted approach that includes revising pricing strategies, managing costs more effectively, and anticipating changes in consumer demand.
In the short term, manufacturers may feel pressured to increase vehicle prices to offset the financial burdens imposed by tariffs, which could deter potential buyers and curtail sales. However, a myopic focus on immediate financial recovery could prove detrimental in the long run. Instead, manufacturers should engage in rigorous forecasting to assess long-term impacts on profitability and operational sustainability within a competitive market environment.
Strategic planning must focus on the integration of innovative practices as well as the exploration of alternative sourcing and production methodologies. By proactively preparing for potential repercussions of ongoing tariff adjustments and economic shifts, truck manufacturers can maintain their competitive edge while safeguarding their market position.
The trucking industry is at a crossroads, and only those information and analytics-driven manufacturers who embrace change and pivot their operational strategies will be able to thrive amidst these challenges. Ultimately, the ability to adapt and strategically plan for both current and future uncertainties will be the defining factor in determining the profitability and resilience of truck manufacturers in this rapidly evolving landscape.
User Adoption Data Statistics in the Trucking Market Post-Tariffs
The implementation of tariffs in the trucking sector has induced significant changes that can be quantified through various statistics affecting user adoption, purchases, and operational strategies. Here are the key findings:
Truck Purchases and Fleet Management
- Decline in Truck Deliveries: Companies like Volvo Group have adjusted their forecasts for heavy truck deliveries in North America, projecting 265,000 units for 2025, a decrease of 10,000 units from earlier estimates. This contraction is mainly attributed to declining freight volumes, high tariff costs, and regulatory uncertainties. [Source: Reuters]
- Fleet Reductions: In light of challenging market conditions, carriers have reduced their fleets by an average of 2.2%. For example, Marten Transport slashed its total fleet from 3,126 tractors to 2,928 over the span of a year, indicating a cautious approach towards fleet expansion amidst rising costs. [Source: CCJ Digital]
Consumer Behavior and Market Shifts
- Rise of Private Fleets: There has been an 11.7% year-over-year increase in shipments from private fleets in 2024, reflecting shippers’ preference for tighter control over their logistics amid tariff uncertainties. This trend demonstrates a shift away from reliance on traditional freight carriers towards more secure, self-managed transport solutions. [Source: Entourage Freight Solutions]
- Freight Volume Fluctuations: The trucking industry saw a temporary boom in shipments due to stockpiling ahead of tariff implementations. Nevertheless, this was succeeded by a downturn, with national shipments down 9.8% and spending falling by 4.9% in the second quarter of 2025 compared to the same quarter the previous year. [Source: Food Logistics]
Overall Market Dynamics
- Increased Operational Costs: The tariffs have raised the cost of truck manufacturing and maintenance, with estimates suggesting that a 25% tariff could inflate tractor prices by approximately $35,000. Larger fleets particularly feel the strain, which affects their annual operational budgets heavily. [Source: Fleet Connection]
- Declining Port Activity: U.S. ports project a decrease in import volumes, anticipating container imports to dip below 2 million TEUs monthly through late 2025. This reduction directly influences trucking demand, especially in facilities reliant on drayage and intermodal transport. [Source: Luna Logistics]
In conclusion, the post-tariff landscape has led to diminishing truck purchases, strategic cutbacks in fleet sizes, an inclination towards private logistical solutions, and surging operational expenses—all of which are reshaping the U.S. trucking market significantly.
Quotes from Industry Leaders
The commentary on the impact of tariffs on the trucking industry is further enriched by insights from industry leaders:
Donald Trump, former President of the United States, emphasized the need for protective measures for American manufacturers, stating:
“In order to protect our Great Heavy Truck Manufacturers from unfair outside competition, I will be imposing a 25% Tariff on all ‘Heavy (Big!) Trucks’ made in other parts of the World.”
He also added, “We need our Truckers to be financially healthy and strong, for many reasons, but above all else, for National Security purposes!” This reveals the administration’s focus on supporting domestic production against foreign competition.
Peter Voorhoeve, President of Volvo Trucks North America, confronted the realities imposed by such tariffs when he stated:
“That doesn’t really cover all the cost [of the tariffs], but that’s all we can do for the moment. It puts pressure on margins…”
His remarks highlight the challenges that manufacturers face in compensating for increased costs due to tariffs without fully passing those burdens onto consumers. Voorhoeve also mentioned, “Heavy-duty truck orders continue to be negatively affected by market uncertainty about freight rates and demand, possible regulatory changes, and the impact of tariffs.” This expresses concern over how tariffs create market instability that can affect orders and profitability within the trucking sector.
These quotes underscore the complex and multifaceted impact of tariffs on the trucking industry, illustrating the differing perspectives of industry leaders and the significant stakes involved.
National Security Implications of Tariffs on Heavy Trucks
The imposition of a 25% tariff on heavy trucks not made in the U.S. reflects a significant intersection between economic policy and national security considerations. As global supply chains become increasingly intricate, the reasoning behind tariffs extends beyond mere economic interests, delving into the safeguarding of American manufacturing capabilities and ensuring the resilience of critical industries that underpin national security.
Firstly, the tariffs aim to bolster domestic manufacturing and reduce dependence on foreign-produced vehicles. By protecting American truck manufacturers from foreign competition, the U.S. government seeks to revitalize a sector considered essential for logistics and transportation. The trucking industry is foundational to the American economy, responsible for moving approximately 70% of freight tonnage. Ensuring its stability is crucial for national defense logistics, as military operations rely heavily on a robust transportation network.
By enhancing the competitiveness of American truck manufacturers such as Paccar and Mack Trucks, the tariffs not only support job preservation but also foster a manufacturing base that can meet national needs in times of crisis. A strong domestic trucking sector can respond swiftly to emergencies—whether in military mobilization or disaster relief—without reliance on uncertain international supply chains. This ties into broader U.S. economic policies focused on cultivating self-sufficiency and resilience against global supply shocks.
Furthermore, these tariffs resonate with a growing trend among policymakers to prioritize economic nationalism. There is a belief that protecting homegrown industries is essential for safeguarding national interests, which includes securing the supply of vehicles for defense and emergency purposes. For instance, in the event of geopolitical tensions or conflicts, having robust national manufacturing capabilities can ensure continued access to critical transportation resources without dependence on foreign entities.
On the flip side, while the tariffs aim to protect domestic industries, they may also provoke retaliatory measures by trading partners, potentially straining international relations. It’s crucial to balance protective trade measures with diplomacy to avoid escalating trade tensions that might inadvertently compromise national security.
In summary, the national security implications of the tariffs on heavy trucks underscore the necessity of a strong domestic manufacturing base and the importance of self-reliance in critical industries. The intertwining of economic policy and national security not only shapes the future trajectory of American manufacturing but also defines the nation’s ability to navigate an increasingly unpredictable global landscape.
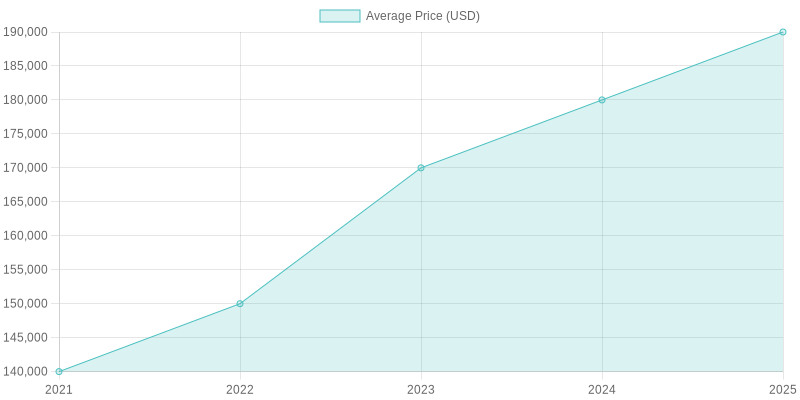
Graph illustrating pricing trends of heavy trucks, including projected price increases due to the 25% tariff.
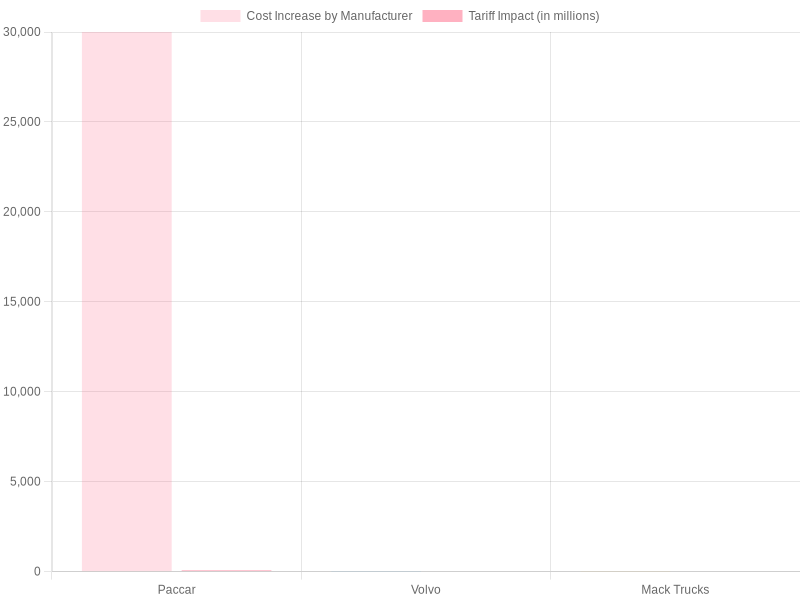
Graph showing the potential impact of tariffs on the truck manufacturing industry, highlighting different manufacturers’ responses.
Call to Action
As the trucking industry grapples with the implications of tariffs, staying informed is paramount. To dive deeper into the impact of these tariffs and access detailed statistics related to truck pricing and profitability, we recommend reviewing the following insightful industry reports:
- Tariffs Impact on Trucking Industry: What We Know So Far
- ATRI Report: Rising Costs Continue to Squeeze Trucking Industry
- Tariffs Disrupt Trucking Industry Dynamics
These resources provide comprehensive insights that will help stakeholders make informed decisions in navigating the financial challenges posed by tariffs and changing market dynamics.